#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n, t, sum = 0, remainder;
{
int n, t, sum = 0, remainder;
printf("Enter an integer\n");
scanf("%d", &n);
scanf("%d", &n);
t = n;
while (t != 0)
{
remainder = t % 10;
sum = sum + remainder;
t = t / 10;
}
{
remainder = t % 10;
sum = sum + remainder;
t = t / 10;
}
printf("Sum of digits of %d = %d\n", n, sum);
return 0;
}
}
If you wish you can modify the input variable (n) and without using an additional variable (t) but it isn't recommended.
Output of program:
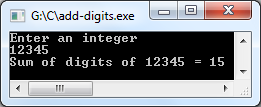

Calculate sum of digits in C without modulus operator
C program to find the sum of digit(s) of an integer that does not use modulus operator. Our program uses a character array (string) for storing an integer. We convert every character of the string into an integer and add all these integers.
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int c, sum, t;
char n[1000];
printf("Input an integer\n");
scanf("%s", n);
sum = c = 0;
while (n[c] != '\0') {
t = n[c] - '0'; // Converting character to integer
sum = sum + t;
c++;
}
printf("Sum of digits of %s = %d\n", n, sum);
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int c, sum, t;
char n[1000];
printf("Input an integer\n");
scanf("%s", n);
sum = c = 0;
while (n[c] != '\0') {
t = n[c] - '0'; // Converting character to integer
sum = sum + t;
c++;
}
printf("Sum of digits of %s = %d\n", n, sum);
return 0;
}
An advantage of this method is that the input integer can be very large which can't be stored in an int or a long long variable, see an example below.
Output of program:
Input an integer
123456789123456789123456789
Sum of digits of 123456789123456789123456789 = 135
123456789123456789123456789
Sum of digits of 123456789123456789123456789 = 135
Sum of digits of a number C program using recursion
#include <stdio.h>
int add_digits(int);
int main()
{
int n, result;
{
int n, result;
scanf("%d", &n);
result = add_digits(n);
printf("%d\n", result);
return 0;
}
}
int add_digits(int n) {
static int sum = 0;
static int sum = 0;
if (n == 0) {
return 0;
}
return 0;
}
sum = n%10 + add_digits(n/10);
return sum;
}
}
The static variable sum is used and initialized to 0; its value will persist after function calls, i.e., it is initialized once when the function is called for the first time.
No comments:
Post a Comment