#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int c, n, f = 1;
printf("Enter a number to calculate its factorial\n");
scanf("%d", &n);
int main()
{
int c, n, f = 1;
printf("Enter a number to calculate its factorial\n");
scanf("%d", &n);
for (c = 1; c <= n; c++)
f = f * c;
printf("Factorial of %d = %d\n", n, f);
return 0;
}
f = f * c;
printf("Factorial of %d = %d\n", n, f);
return 0;
}
Output of C factorial program:
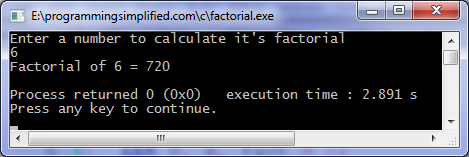
Factorial program in C using recursion
#include<stdio.h>
long factorial(int);
int main()
{
int n;
long f;
printf("Enter an integer to find its factorial\n");
scanf("%d", &n);
if (n < 0)
printf("Factorial of negative integers isn't defined.\n");
else
{
f = factorial(n);
printf("%d! = %ld\n", n, f);
}
return 0;
}
long factorial(int);
int main()
{
int n;
long f;
printf("Enter an integer to find its factorial\n");
scanf("%d", &n);
if (n < 0)
printf("Factorial of negative integers isn't defined.\n");
else
{
f = factorial(n);
printf("%d! = %ld\n", n, f);
}
return 0;
}
long factorial(int n)
{
if (n == 0) // Base case
return 1;
else
return (n*factorial(n-1));
}
{
if (n == 0) // Base case
return 1;
else
return (n*factorial(n-1));
}
In recursion, a function calls itself. In the above program, the factorial function is calling itself. To solve a problem using recursion, you must first express its solution in recursive form.
C program to find factorial of a number
#include <stdio.h>
long factorial(int);
int main()
{
int n;
{
int n;
printf("Enter a number to calculate its factorial\n");
scanf("%d", &n);
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("%d! = %ld\n", n, factorial(n));
return 0;
}
}
long factorial(int n)
{
int c;
long r = 1;
{
int c;
long r = 1;
for (c = 1; c <= n; c++)
r = r * c;
r = r * c;
return r;
}
}
No comments:
Post a Comment