#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n, sum = 0, c, value;
printf("How many numbers you want to add?\n");
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("Enter %d integers\n", n);
for (c = 1; c <= n; c++)
{
scanf("%d", &value);
sum = sum + value;
}
printf("Sum of the integers = %d\n", sum);
return 0;
}
int main()
{
int n, sum = 0, c, value;
printf("How many numbers you want to add?\n");
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("Enter %d integers\n", n);
for (c = 1; c <= n; c++)
{
scanf("%d", &value);
sum = sum + value;
}
printf("Sum of the integers = %d\n", sum);
return 0;
}
You can use long int or long long data type for the variable sum.
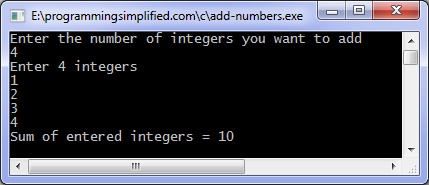
Output of program:
calculate sum of n numbers using an array
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n, sum = 0, c, array[100];
{
int n, sum = 0, c, array[100];
scanf("%d", &n);
for (c = 0; c < n; c++)
{
scanf("%d", &array[c]);
sum = sum + array[c];
}
{
scanf("%d", &array[c]);
sum = sum + array[c];
}
printf("Sum = %d\n", sum);
return 0;
}
}
The advantage of using an array is that we have a record of the numbers entered and can use them further in the program if required but storing them requires additional memory.
C program for addition of n numbers using recursion
#include <stdio.h>
long calculate_sum(int [], int);
int main()
{
int n, c, array[100];
long result;
{
int n, c, array[100];
long result;
scanf("%d", &n);
for (c = 0; c < n; c++)
scanf("%d", &array[c]);
scanf("%d", &array[c]);
result = calculate_sum(array, n);
printf("Sum = %ld\n", result);
return 0;
}
}
long calculate_sum(int a[], int n) {
static long sum = 0;
static long sum = 0;
if (n == 0)
return sum;
return sum;
sum = sum + a[n-1];
return calculate_sum(a, --n);
}
}
No comments:
Post a Comment