C program to reverse an array: This program reverses the array elements. For example, if 'A' is an array of integers with three elements such that
A[0] = 1, A[1] = 2, A[2] = 3
Then after reversing, the array will be
A[0] = 3, A[1] = 2, A[0] = 1
A[0] = 1, A[1] = 2, A[2] = 3
Then after reversing, the array will be
A[0] = 3, A[1] = 2, A[0] = 1
Reverse array C program
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n, c, d, a[100], b[100];
{
int n, c, d, a[100], b[100];
printf("Enter the number of elements in array\n");
scanf("%d", &n);
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("Enter array elements\n");
for (c = 0; c < n ; c++)
scanf("%d", &a[c]);
scanf("%d", &a[c]);
/*
* Copying elements into array b starting from end of array a
*/
* Copying elements into array b starting from end of array a
*/
for (c = n - 1, d = 0; c >= 0; c--, d++)
b[d] = a[c];
b[d] = a[c];
/*
* Copying reversed array into the original.
* Here we are modifying original array, this is optional.
*/
* Copying reversed array into the original.
* Here we are modifying original array, this is optional.
*/
for (c = 0; c < n; c++)
a[c] = b[c];
a[c] = b[c];
printf("Reverse array is\n");
for (c = 0; c < n; c++)
printf("%d\n", a[c]);
printf("%d\n", a[c]);
return 0;
}
}
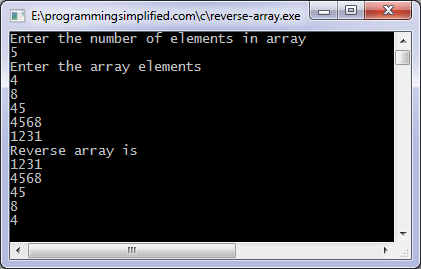
Reverse array C program output:

Reverse array by swapping (without using additional memory)
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int array[100], n, c, t, end;
int array[100], n, c, t, end;
scanf("%d", &n);
end = n - 1;
end = n - 1;
for (c = 0; c < n; c++) {
scanf("%d", &array[c]);
}
scanf("%d", &array[c]);
}
for (c = 0; c < n/2; c++) {
t = array[c];
array[c] = array[end];
array[end] = t;
t = array[c];
array[c] = array[end];
array[end] = t;
end--;
}
}
printf("Reversed array elements are:\n");
for (c = 0; c < n; c++) {
printf("%d\n", array[c]);
}
printf("%d\n", array[c]);
}
return 0;
}
}
C program to reverse an array using pointers
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
void reverse_array(int*, int);
int main()
{
int n, c, *pointer;
scanf("%d",&n);
pointer = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*n);
if( pointer == NULL )
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
for ( c = 0 ; c < n ; c++ )
scanf("%d",(pointer+c));
reverse_array(pointer, n);
printf("Original array on reversal is\n");
for ( c = 0 ; c < n ; c++ )
printf("%d\n",*(pointer+c));
free(pointer);
return 0;
}
{
int n, c, *pointer;
scanf("%d",&n);
pointer = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*n);
if( pointer == NULL )
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
for ( c = 0 ; c < n ; c++ )
scanf("%d",(pointer+c));
reverse_array(pointer, n);
printf("Original array on reversal is\n");
for ( c = 0 ; c < n ; c++ )
printf("%d\n",*(pointer+c));
free(pointer);
return 0;
}
void reverse_array(int *pointer, int n)
{
int *s, c, d;
s = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*n);
if( s == NULL )
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
for ( c = n - 1, d = 0 ; c >= 0 ; c--, d++ )
*(s+d) = *(pointer+c);
for ( c = 0 ; c < n ; c++ )
*(pointer+c) = *(s+c);
free(s);
}
{
int *s, c, d;
s = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*n);
if( s == NULL )
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
for ( c = n - 1, d = 0 ; c >= 0 ; c--, d++ )
*(s+d) = *(pointer+c);
for ( c = 0 ; c < n ; c++ )
*(pointer+c) = *(s+c);
free(s);
}
No comments:
Post a Comment