#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int array[100], n, c, d, swap;
{
int array[100], n, c, d, swap;
printf("Enter number of elements\n");
scanf("%d", &n);
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("Enter %d integers\n", n);
for (c = 0; c < n; c++)
scanf("%d", &array[c]);
scanf("%d", &array[c]);
for (c = 0 ; c < n - 1; c++)
{
for (d = 0 ; d < n - c - 1; d++)
{
if (array[d] > array[d+1]) /* For decreasing order use < */
{
swap = array[d];
array[d] = array[d+1];
array[d+1] = swap;
}
}
}
{
for (d = 0 ; d < n - c - 1; d++)
{
if (array[d] > array[d+1]) /* For decreasing order use < */
{
swap = array[d];
array[d] = array[d+1];
array[d+1] = swap;
}
}
}
printf("Sorted list in ascending order:\n");
for (c = 0; c < n; c++)
printf("%d\n", array[c]);
printf("%d\n", array[c]);
return 0;
}
}
Output of program:
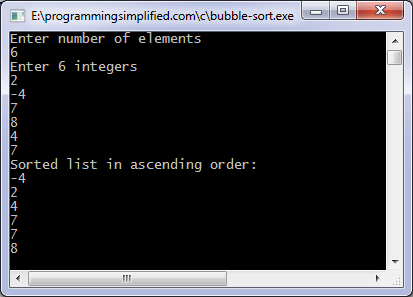
Other sorting algorithms:
Selection sort in C
Insertion sort in C
Selection sort in C
Insertion sort in C
Bubble sort program in C language using function
#include <stdio.h>
void bubble_sort(long [], long);
int main()
{
long array[100], n, c;
{
long array[100], n, c;
printf("Enter number of elements\n");
scanf("%ld", &n);
scanf("%ld", &n);
printf("Enter %ld integers\n", n);
for (c = 0; c < n; c++)
scanf("%ld", &array[c]);
scanf("%ld", &array[c]);
bubble_sort(array, n);
printf("Sorted list in ascending order:\n");
for (c = 0; c < n; c++)
printf("%ld\n", array[c]);
printf("%ld\n", array[c]);
return 0;
}
}
void bubble_sort(long list[], long n)
{
long c, d, t;
{
long c, d, t;
for (c = 0 ; c < n - 1; c++) {
for (d = 0 ; d < n - c - 1; d++) {
if (list[d] > list[d+1]) {
/* Swapping */
t = list[d];
list[d] = list[d+1];
list[d+1] = t;
}
}
}
}
for (d = 0 ; d < n - c - 1; d++) {
if (list[d] > list[d+1]) {
/* Swapping */
t = list[d];
list[d] = list[d+1];
list[d+1] = t;
}
}
}
}
We can use the Bubble Sort algorithm to check if an array is sorted or not. If no swapping takes place, then the array is sorted. We can improve its best-case complexity (if the array is already sorted) to O(n).
#include <stdio.h>
int is_Array_Sorted(int [], int);
int main()
{
int a[100], n, c;
{
int a[100], n, c;
printf("Enter number of elements\n");
scanf("%d", &n);
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("Enter %d integers\n", n);
for (c = 0; c < n; c++)
scanf("%d", &a[c]);
scanf("%d", &a[c]);
if (is_Array_Sorted(a, n))
printf("The array is sorted.\n");
else
printf("The array isn't sorted.\n");
printf("The array is sorted.\n");
else
printf("The array isn't sorted.\n");
return 0;
}
}
int is_Array_Sorted(int a[], int n) {
int c, d, sorted = 1, t;
int c, d, sorted = 1, t;
for (c = 0 ; c < n - 1; c++) {
for (d = 0 ; d < n - c - 1; d++) {
if (a[d] > a[d+1]) {
t = a[d];
a[d] = a[d+1];
a[d+1] = t;
return 0;
}
}
}
return 1;
}
for (d = 0 ; d < n - c - 1; d++) {
if (a[d] > a[d+1]) {
t = a[d];
a[d] = a[d+1];
a[d+1] = t;
return 0;
}
}
}
return 1;
}
No comments:
Post a Comment